The chemical island of Huaneng Tianjin IGCC Power Plant 250MW unit includes air separation system, gasification system, desulfurization and sulfur recovery system. The gasification system includes subsystems such as coal grinding and drying, pulverized coal pressurization and transportation, gasification/syngas cooling, slag discharge, dry ash removal, wet scrubbing, and preliminary water treatment. The gasifier is a two-stage gasifier. The DCS unit uses PKSDCS manufactured by Honeywell.
The pulverized coal conveying system adopts independent three pipelines, in which pipelines A and B respectively transport pulverized coal to a gasifier, and pipeline C transports pulverized coal to the second-stage gasifier. According to the designed coal, A and B pipelines provide 50% gasifier production design coal, and C pipelines provide 15% gasifier production capacity of design coal. The relevant control of the pulverized coal conveying system includes sequential control, complex control, simple control and interlocking control logic.
First, the sequence of control 1.1 Sequence Control Program Dry pulverized coal conveying system The main equipment is pulverized coal bag filter, pulverized coal storage tank, discharge tank and feeding tank, the system structure shown in Figure 1.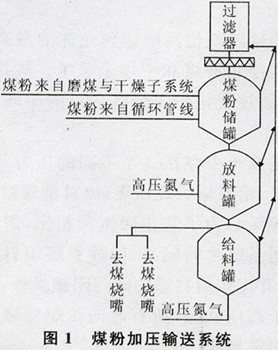
The dry pulverized coal pressurization conveying process is realized by a sequential feeding control program and corresponds to A, B, and C pipelines, respectively. During normal operation, the pulverized coal pressurized transfer process is controlled by a sequential feed control program. The feed control program automatically opens the feed valve according to the coal burner's demand for pulverized coal, and feeds the feed tank intermittently.
The sequential feeding control program has 18 steps. Each step includes execution conditions and action instructions. Before starting the feed control procedure, after confirming that the feed tank is in the high-pressure full tank state, the following control is performed:
(1) As the feed tank continuously sends the pulverized coal to the coal burner, its material level keeps dropping. When the material level drops below the set value, the bottom valve of the feed tank is opened to feed the material to the feed tank and start Discharge timer.
(2) If the feed tank is empty during the counting time, isolate the feed tank and the feed tank by closing the discharge valve and the balance valve, and then open the pressure reducing valve to gradually depressurize the discharge tank. The depressurization process is divided into 3 steps. Sequentially, the nitrogen gas is discharged into the atmosphere through the pulverized coal filter through the orifice plate and shut-off valve in the first two steps, and the third step ensures the discharge tank and the feed tank through the balance valve between the discharge tank and the filter. Pressure balance between tanks.
(3) Turn on the valve at the bottom of the pulverized coal tank. Pulverized coal flows into the discharge tank by gravity.
(4) After the material level of the discharge tank reaches the set value, close the packing valve and the balancing valve to isolate the powdered coal storage tank and the discharge tank.
(5) Open the high-pressure nitrogen valve at the bottom of the discharge tank and the top of the tank to repressurize the discharge tank until the pressure in the discharge tank and the feed tank are the same, and the pressure between the discharge tank and the feed tank is opened. The pipeline balances the pressure.
(6) The coal grinding and drying subsystem continuously feeds the pulverized coal storage tanks.
1.2 Bridge Removal Procedure After the discharge timer expires, if the discharge tank cannot be emptied, it indicates that there is a bridge between the discharge tank and the feed tank, and the control system will automatically start the bridge removal process. Open the bottom of the feed tank to the nitrogen valve of the pipe purifier and the nitrogen valve to the air distributor. At the same time, start the eliminator timer. During the eliminator, close the valve isolation pot on the bottom of the feed tank and the balance line. In the tank, after the bridge process ends, the nitrogen valve is closed and the pressure equalization line between the discharge tank and the feed tank is reopened. Before the timer expires, if the emptying tank is empty, it will re-enter the sequence control program; otherwise it will enter the bridge removal process. The control program allows two bridge removal processes. After the two bridge removal program operation cycles have ended, the discharge tank is still not cleared, and the program is stopped and an audible alarm is issued. At this point, the operator has two options: (1) If the low level signal of the feed tank disappears, the low level signal is simulated. (2) If the low level signal of the feed tank still exists and there is no feed tank low level signal, restart the bridge removal process.
Second, the complex control 2.1 Feeding cans ventilation vertebral nitrogen flow control At the bottom of the feeding tank set up a ventilation vertebrae, nitrogen through the nitrogen control valve to the ventilation vertebrae, in order to ensure the stability of the pulverized coal discharge flow to the feed tank. Under normal circumstances, the high-pressure nitrogen control valve is controlled by the flow rate. When the ventilation cone pipe is blocked or other reasons cause the pressure difference on both sides of the ventilator to increase, in order to ensure that the ventilator does not break and damage, the control system cuts to the pressure difference control. Feeder aeration cone nitrogen flow control shown in Figure 2.
2.2 Feed tank pressure control The feed tank is equipped with a pressure control valve, which uses two control methods: pressure and pressure difference. During the purging of the gasifier, the pulverized coal is circulated back to the conveying system by the circulation line, and pressure control is used at this time. When starting the coal burner to ignite, in order to maintain the pressure difference between the feed tank and the gasifier, a pressure difference control method is adopted. Pressurize the feed tank through the A pressurizing valve or drain the pulverized coal filter through the B pressure relief valve to maintain the feed tank pressure within the set value range. The feed tank pressure control logic is shown in Figure 3.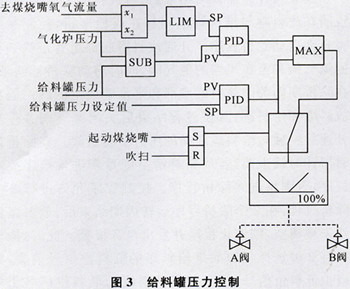
Third, simple control of the discharge tank using high-pressure nitrogen pressure, part of the nitrogen through the bottom of the ventilator directly into the tank, in order to protect the ventilation of the ventilator plate, in the nitrogen pressure line is set on the pressure control valve. The differential pressure control valve controls the nitrogen pressure entering the ventilator and the pressure difference at the top of the discharge tank during the pressurization or removal of the bridge. This control only receives the sequence control program start and stop instructions.
Before the balance line between the discharge tank and the feed tank is connected, the pressure balance control between the feed tank and the discharge tank can be achieved by adjusting the discharge amount of the discharge tank to the pulverized coal filter. This control is used only during the sequence control program input.
IV. Interlock Control If the height of the pulverized coal storage tank reaches the maximum allowable level, the interlocking control stops the coal grinding and drying subsystems. During the start-up and shutdown of the gasifier, pulverized coal is returned to the pulverized coal storage tank through the circulation line of the coal burner inlet of the gasification furnace.
There are two different pressure levels in the conveying system. The pulverized coal storage tank is of low pressure level and the feeding tank is of high pressure level. The discharging amount tank switches the pressure level according to the amount of filling material. In order to prevent backflow and overpressure, it is necessary to always ensure the isolation between the low pressure and high pressure systems, ie, the low pressure during the filling of the discharge tank, and all the valves connected to the feed tank are locked to operate; the discharge tank is in a high pressure state during discharge, all The valves leading to pulverized coal tanks and pulverized coal filters are locked.
The pulverized coal conveying system adopts independent three pipelines, in which pipelines A and B respectively transport pulverized coal to a gasifier, and pipeline C transports pulverized coal to the second-stage gasifier. According to the designed coal, A and B pipelines provide 50% gasifier production design coal, and C pipelines provide 15% gasifier production capacity of design coal. The relevant control of the pulverized coal conveying system includes sequential control, complex control, simple control and interlocking control logic.
First, the sequence of control 1.1 Sequence Control Program Dry pulverized coal conveying system The main equipment is pulverized coal bag filter, pulverized coal storage tank, discharge tank and feeding tank, the system structure shown in Figure 1.

The dry pulverized coal pressurization conveying process is realized by a sequential feeding control program and corresponds to A, B, and C pipelines, respectively. During normal operation, the pulverized coal pressurized transfer process is controlled by a sequential feed control program. The feed control program automatically opens the feed valve according to the coal burner's demand for pulverized coal, and feeds the feed tank intermittently.
The sequential feeding control program has 18 steps. Each step includes execution conditions and action instructions. Before starting the feed control procedure, after confirming that the feed tank is in the high-pressure full tank state, the following control is performed:
(1) As the feed tank continuously sends the pulverized coal to the coal burner, its material level keeps dropping. When the material level drops below the set value, the bottom valve of the feed tank is opened to feed the material to the feed tank and start Discharge timer.
(2) If the feed tank is empty during the counting time, isolate the feed tank and the feed tank by closing the discharge valve and the balance valve, and then open the pressure reducing valve to gradually depressurize the discharge tank. The depressurization process is divided into 3 steps. Sequentially, the nitrogen gas is discharged into the atmosphere through the pulverized coal filter through the orifice plate and shut-off valve in the first two steps, and the third step ensures the discharge tank and the feed tank through the balance valve between the discharge tank and the filter. Pressure balance between tanks.
(3) Turn on the valve at the bottom of the pulverized coal tank. Pulverized coal flows into the discharge tank by gravity.
(4) After the material level of the discharge tank reaches the set value, close the packing valve and the balancing valve to isolate the powdered coal storage tank and the discharge tank.
(5) Open the high-pressure nitrogen valve at the bottom of the discharge tank and the top of the tank to repressurize the discharge tank until the pressure in the discharge tank and the feed tank are the same, and the pressure between the discharge tank and the feed tank is opened. The pipeline balances the pressure.
(6) The coal grinding and drying subsystem continuously feeds the pulverized coal storage tanks.
1.2 Bridge Removal Procedure After the discharge timer expires, if the discharge tank cannot be emptied, it indicates that there is a bridge between the discharge tank and the feed tank, and the control system will automatically start the bridge removal process. Open the bottom of the feed tank to the nitrogen valve of the pipe purifier and the nitrogen valve to the air distributor. At the same time, start the eliminator timer. During the eliminator, close the valve isolation pot on the bottom of the feed tank and the balance line. In the tank, after the bridge process ends, the nitrogen valve is closed and the pressure equalization line between the discharge tank and the feed tank is reopened. Before the timer expires, if the emptying tank is empty, it will re-enter the sequence control program; otherwise it will enter the bridge removal process. The control program allows two bridge removal processes. After the two bridge removal program operation cycles have ended, the discharge tank is still not cleared, and the program is stopped and an audible alarm is issued. At this point, the operator has two options: (1) If the low level signal of the feed tank disappears, the low level signal is simulated. (2) If the low level signal of the feed tank still exists and there is no feed tank low level signal, restart the bridge removal process.
Second, the complex control 2.1 Feeding cans ventilation vertebral nitrogen flow control At the bottom of the feeding tank set up a ventilation vertebrae, nitrogen through the nitrogen control valve to the ventilation vertebrae, in order to ensure the stability of the pulverized coal discharge flow to the feed tank. Under normal circumstances, the high-pressure nitrogen control valve is controlled by the flow rate. When the ventilation cone pipe is blocked or other reasons cause the pressure difference on both sides of the ventilator to increase, in order to ensure that the ventilator does not break and damage, the control system cuts to the pressure difference control. Feeder aeration cone nitrogen flow control shown in Figure 2.

2.2 Feed tank pressure control The feed tank is equipped with a pressure control valve, which uses two control methods: pressure and pressure difference. During the purging of the gasifier, the pulverized coal is circulated back to the conveying system by the circulation line, and pressure control is used at this time. When starting the coal burner to ignite, in order to maintain the pressure difference between the feed tank and the gasifier, a pressure difference control method is adopted. Pressurize the feed tank through the A pressurizing valve or drain the pulverized coal filter through the B pressure relief valve to maintain the feed tank pressure within the set value range. The feed tank pressure control logic is shown in Figure 3.

Third, simple control of the discharge tank using high-pressure nitrogen pressure, part of the nitrogen through the bottom of the ventilator directly into the tank, in order to protect the ventilation of the ventilator plate, in the nitrogen pressure line is set on the pressure control valve. The differential pressure control valve controls the nitrogen pressure entering the ventilator and the pressure difference at the top of the discharge tank during the pressurization or removal of the bridge. This control only receives the sequence control program start and stop instructions.
Before the balance line between the discharge tank and the feed tank is connected, the pressure balance control between the feed tank and the discharge tank can be achieved by adjusting the discharge amount of the discharge tank to the pulverized coal filter. This control is used only during the sequence control program input.
IV. Interlock Control If the height of the pulverized coal storage tank reaches the maximum allowable level, the interlocking control stops the coal grinding and drying subsystems. During the start-up and shutdown of the gasifier, pulverized coal is returned to the pulverized coal storage tank through the circulation line of the coal burner inlet of the gasification furnace.
There are two different pressure levels in the conveying system. The pulverized coal storage tank is of low pressure level and the feeding tank is of high pressure level. The discharging amount tank switches the pressure level according to the amount of filling material. In order to prevent backflow and overpressure, it is necessary to always ensure the isolation between the low pressure and high pressure systems, ie, the low pressure during the filling of the discharge tank, and all the valves connected to the feed tank are locked to operate; the discharge tank is in a high pressure state during discharge, all The valves leading to pulverized coal tanks and pulverized coal filters are locked.
ZHEJIANG FULE MINING MACHINERY CO., LTD , https://www.flmachines.com